Transportation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Book | ||
| image | |image=Transportation1Chapter.jpg | ||
| blueprint | |poc=Wilfred Pinfold | ||
| | |authors=Wilfred Pinfold, Skip Newberry, Jeff Allen, Ken Montler, Timothy Smith, Joe Cortright, Greta Knappenberger, Jill Sorensen, John Feo, Corey Marshall, Jose Gonzalez, Geoffrey Urbach | ||
|blueprint=Transportation | |||
|chapter=700 | |||
|sectors=Transportation | |||
|summary=National transportation systems are a network of roads, highways, railways, airports, and waterways that enables the movement of people and goods throughout and between countries. They are complex system that includes various modes of transportation, such as air, rail, road, and water, and are essential to the functioning of the country's economy. | |||
}} | |||
There are several different modes of transportation that make up the national transportation system of the United States. These include: | |||
*'''Road''': This includes highways, streets, and roads that are used by cars, trucks, buses, and other vehicles to travel from one place to another. | |||
*'''Rail''': This includes trains that run on tracks and are used to transport people and goods across the country. | |||
*'''Air''': This includes airplanes and other aircraft that are used to transport people and goods through the air. | |||
*'''Water''': This includes ships, boats, and other watercraft that are used to transport people and goods across bodies of water, such as oceans and rivers. | |||
*'''Public transit''': This includes buses, subways, and other forms of mass transit that are used to transport people within cities and other urban areas. | |||
*'''[[Active Transit]]''': This includes paths, lanes, and other infrastructure that is dedicated to the use of bicycles and pedestrians. | |||
*'''Intermodal''': This refers to the use of multiple modes of transportation, such as shipping goods by truck to a port where they are then loaded onto a ship for transport by water. | |||
In the United States the national transportation system is overseen by the Department of Transportation (DOT) and various other agencies at the federal, state, and local levels. As of 2021, the United States had | |||
*More than 4 million miles of roads, including over 160,000 miles of interstate highways. | |||
*Approximately 30,000 miles of railroads, including both freight and passenger lines. | |||
*Over 19,000 airports, including more than 500 commercial airports. | |||
*More than 25,000 miles of waterways, including rivers, canals, and the Great Lakes. | |||
The U.S. transportation system supports a large and diverse economy, with goods valued at over $22 trillion shipped by various modes of transportation in 2019 including | |||
*A diverse fleet of vehicles, including over 250 million cars and trucks. | |||
*A total number of passenger trips on public transportation of 10.8 billion. | |||
*Over 940 million passengers travelling on U.S. airlines. | |||
Transportation systems are changing rapidly. There are many emerging technologies and trends that are expected to shape the future. Some of the key trends include: | |||
*'''[[Autonomous Vehicles]]''': Self-driving cars, trucks, and other vehicles are expected to become more common in the coming years. These vehicles use sensors, cameras, and other technologies to navigate roads and make decisions without human input. | |||
*'''[[Connected Vehicles]]''': Connected vehicles are vehicles that are equipped with sensors, cameras, and other technologies that allow them to communicate with each other and with infrastructure such as traffic lights and road signs. The goal of connected vehicles is to improve safety, reduce traffic congestion, and make transportation more efficient. | |||
*'''[[Electric and Hybrid Vehicles]]''': There is growing interest in electric and hybrid vehicles as a way to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and reduce emissions. These vehicles use electricity and/or alternative fuels to power their engines. | |||
*'''[[High Speed Rail]]''': High-speed rail systems, which can travel at speeds of over 200 miles per hour, are being developed in several countries and are expected to become more widespread in the future. | |||
*'''[[Hyperloop]]''': The Hyperloop is a proposed mode of transportation that would use a network of tubes to transport people and goods at high speeds. | |||
*'''[[Urban Air Mobility]]''': Companies are developing electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft and other technologies to enable the use of small aircraft for short trips within cities. | |||
*'''[[Shared Mobility]]''': Services such as ride-hailing and bike-sharing are expected to become more prevalent, offering convenient and affordable transportation options for short trips. | |||
=Activities= | |||
{{#ask: | |||
[[Category:Activity]] | |||
[[Category:{{PAGENAME}}]] | |||
|?=# | |||
|?Has image#=2 | |||
|?Has description#=3 | |||
|format=plainlist | |||
|named args=yes | |||
|introtemplate=Show image Header | |||
|template=Show image | |||
|outrotemplate=Show link Footer | |||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:53, January 24, 2023
| Transportation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Introduction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contact | Wilfred Pinfold | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Topics |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEWS
REPORTS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Authors
National transportation systems are a network of roads, highways, railways, airports, and waterways that enables the movement of people and goods throughout and between countries. They are complex system that includes various modes of transportation, such as air, rail, road, and water, and are essential to the functioning of the country's economy.
There are several different modes of transportation that make up the national transportation system of the United States. These include:
- Road: This includes highways, streets, and roads that are used by cars, trucks, buses, and other vehicles to travel from one place to another.
- Rail: This includes trains that run on tracks and are used to transport people and goods across the country.
- Air: This includes airplanes and other aircraft that are used to transport people and goods through the air.
- Water: This includes ships, boats, and other watercraft that are used to transport people and goods across bodies of water, such as oceans and rivers.
- Public transit: This includes buses, subways, and other forms of mass transit that are used to transport people within cities and other urban areas.
- Active Transit: This includes paths, lanes, and other infrastructure that is dedicated to the use of bicycles and pedestrians.
- Intermodal: This refers to the use of multiple modes of transportation, such as shipping goods by truck to a port where they are then loaded onto a ship for transport by water.
In the United States the national transportation system is overseen by the Department of Transportation (DOT) and various other agencies at the federal, state, and local levels. As of 2021, the United States had
- More than 4 million miles of roads, including over 160,000 miles of interstate highways.
- Approximately 30,000 miles of railroads, including both freight and passenger lines.
- Over 19,000 airports, including more than 500 commercial airports.
- More than 25,000 miles of waterways, including rivers, canals, and the Great Lakes.
The U.S. transportation system supports a large and diverse economy, with goods valued at over $22 trillion shipped by various modes of transportation in 2019 including
- A diverse fleet of vehicles, including over 250 million cars and trucks.
- A total number of passenger trips on public transportation of 10.8 billion.
- Over 940 million passengers travelling on U.S. airlines.
Transportation systems are changing rapidly. There are many emerging technologies and trends that are expected to shape the future. Some of the key trends include:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars, trucks, and other vehicles are expected to become more common in the coming years. These vehicles use sensors, cameras, and other technologies to navigate roads and make decisions without human input.
- Connected Vehicles: Connected vehicles are vehicles that are equipped with sensors, cameras, and other technologies that allow them to communicate with each other and with infrastructure such as traffic lights and road signs. The goal of connected vehicles is to improve safety, reduce traffic congestion, and make transportation more efficient.
- Electric and Hybrid Vehicles: There is growing interest in electric and hybrid vehicles as a way to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and reduce emissions. These vehicles use electricity and/or alternative fuels to power their engines.
- High Speed Rail: High-speed rail systems, which can travel at speeds of over 200 miles per hour, are being developed in several countries and are expected to become more widespread in the future.
- Hyperloop: The Hyperloop is a proposed mode of transportation that would use a network of tubes to transport people and goods at high speeds.
- Urban Air Mobility: Companies are developing electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft and other technologies to enable the use of small aircraft for short trips within cities.
- Shared Mobility: Services such as ride-hailing and bike-sharing are expected to become more prevalent, offering convenient and affordable transportation options for short trips.
Activities
|
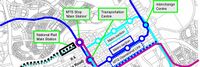
Abuja City Integrated Transportation System | |
| Sustainable Mass Abuja Rapid Transit (SMART) is an easier, efficient and seamless means of utilizing the city’s public mass transit bus service.
Abuja Urban Mass Transit has over 500 buses conveying an estimated 1000 passengers daily. The proposed project will equip 100 buses with devices to generate and transmit real time data and information between drivers, commuters, city transport officials and the general public. The project targets increased ridership and revenue generation from the combination of multiple methods of electronic payments, bus routing, location tracking as well as online bus schedule service. | ||

|
Active Street | |
| The vision to connect the end of the TriMet MAX line in Hillsboro to the Banks-Vernonia State Trail… has been a part of city and regional plans for many years. The section of this trail that runs along an old rail line between Hillsboro and Forrest grove offers some exciting opportunities for this Active Street™ concept. | ||

|
Air Quality Monitoring in London | |
Key Deliverables
| ||

|
Air Quality Sensing Wherever You Go in Taipei | |
The proposed project will develop portable AirBox devices to facilitate mobile air quality monitoring, with a focus on PM2.5 sensing, in Taipei city. The device is small-sized and light-weight, and it uses the LoRa technology for low-power and long-range data communication. The expected results of this project are:
| ||

|
Beaverton Electric Bus Pilot | |
| TriMet purchased five electric buses thanks to a federal grant and support from Portland General Electric. These buses will operate on 62-Murray Blvd in Beaverton. | ||

|
Beverly Public Schools Electric Busses | |
| Beverly Public Schools in Massachusetts has implemented a project utilizing their electric school buses as on-demand power plants. By using bidirectional chargers, the buses' large batteries can both charge and send energy back to the grid, providing backup power during high-demand periods. | ||

|
Bidirectional EV Charging Hub in British Columbia | |
| Pilot Project with BC Hydro, Lion Electric, BorgWarner, PowerTech Labs and Fermata Energy demonstrates Technical Feasibility as a Proof of Concept to Make Vehicle-to-Grid a Reality in British Columbia and Globally | ||

|
Big Data and Artificial Intelligence for Road Infrastructure Sustainability | |
| Provide an efficient and effective solution using artificial intelligence and smartphones to monitor and maintain roadway infrastructure with a data-driven approach. Projects at RoadBotics aim to provide better data and identify which roads are failing and which roads need early intervention in order to avoid total reconstruction. | ||

|
Boring Company Las Vegas Convention Center Loop | |
| The LVCC Loop system — a three-station transportation system consisting of 1.7 miles of tunnel — was built in approximately one year (using the now-legacy Godot Tunnel Boring Machine). LVCC Loop's cost was approximately $47M (firm fixed pricing) for the two tunnels and three stations (two surface and one subsurface). Tunneling occurred during large conventions (>100,000 attendees pre-COVID) with zero road closures and zero attendee disturbances. | ||

|
Brooklyn Smart Energy Hub | |
| The Brooklyn Smart Energy Hub, a collaborative project between First Student and Con Edison, aims to demonstrate a scalable, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) solution to support medium and heavy-duty fleet electrification and address economic barriers in transitioning from diesel to electric power. This innovative hub will integrate 12 electric school buses equipped with rooftop solar panels and a solar array installed on the facility’s roof to create a robust energy generation, battery storage, and delivery system. Utilizing First Student's First Charge technology—a cost-effective, trenchless power deployment approach—the project will reduce installation costs and streamline deployment, even in challenging climates and urban settings. Beyond reducing emissions and operational costs, the hub’s bidirectional charging capabilities will offer backup power during peak demand, emergencies, and for essential services like hospitals, contributing to grid resilience and advancing V2G technology as a critical component of future energy systems. | ||

|
Busan Smart City | |
Key Deliverables
| ||

|
CIVIC Data Platform | |
| CIVIC is an open data platform to democratize
public information and drive meaningful engagement through neutral, nonpartisan analytics. It's built entirely by multidisciplinary teams of volunteer coders, designers and domain experts using open source technology. | ||

|
Cajon Valley Union School District Electric Bus System | |
| San Diego Gas & Electric Cajon Valley Union School District Electric Bus System tests the technology that enables eight electric school buses to put electricity back on the grid when needed such as on hot summer days. A collaborative effort between SDG&E, the Cajon Valley Union School District and locally based technology company Nuvve, this is the first vehicle-to-grid (V2G) project to become operational in Southern California, helping to advance clean air and climate goals while also bolstering grid reliability. | ||

|
Carolinas Alliance 4 Innovation | |
| The Greenville vision is a multimodal and multi-jurisdictional transportation plan across GPATS from Greenville Spartanburg (GSP) airport through Greenville’s urban areas to Clemson University. The modes include elevated, driverless car transit network system (ATN) aka personal rapid transit (PRT); smarter bus transit (including bus and traffic light sensors and electric buses); connected, assisted, or automated LSEV shuttle services; and more bike and pedestrian-friendly pathways. GreenVillages development will occur around mobility hubs. People live in GreenVillages development and connect at transportation nodes to work, shop, learn, heal and play. Better connectivity for people living along urban corridors helps deal with the issues of first/last mile transport so they would not need to own a car, and reduces traffic congestion, air pollution, transportation costs and traffic accidents. | ||
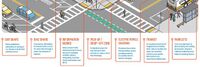
|
City of Boston GoHubs | |
| A majority of our residents rely upon public transit, biking, walking, and driving to get around our city. But, shared mobility and technology advances are altering travel. New ways of transportation are introduced each day. The future of transportation may very well be shared, electric, and highly mobile. GoHubs! are intended to help us organize these modes. We provide information on how to access them and navigate the technology, and ultimately make it easier to get around Boston | ||

|
Community Traffic Guidance and Control System for Natural Disaster Emergency Response | |
| Integrate city-wide traffic monitoring systems, identify disaster area and automate the traffic control over the zone. Research and develop alternative routes for emergency responders, public safety officials and citizens. Provide real time information on traffic to citizens and city decision makers. | ||
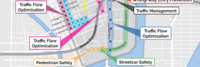
|
Connected Vehicle Pilot Security Management Operating Concept | |
| Development of a Security Management Operating Concept (SMOC) for phase I of the Tampa Hillsborough Expressway Authority (THEA) Connected Vehicle (CV) Pilot Deployment Program. This focuses on how the THEA team developed an approach to the SMOC (i.e., Prepare); categorized information flows and systems (i.e., Categorize); and selected security controls to establish draft, minimum security control baselines (i.e., Select). The resulting SMOC is largely based on the NIST RMF and provides guidance for ensuring “the privacy of pilot participants and the overall security of the Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) system for the THEA CV Pilot.” | ||

|
Direct Air Capture Plant in Oregon | |
| 280 Earth, Inc. has launched its inaugural Direct Air Capture (DAC) facility in The Dalles, Oregon, marking a significant milestone in the fight against climate change. | ||

|
Eastside Crescent Transportation Alliance | |
| The Eastside Crescent Transportation Alliance provides a governance structure for a transportation management Alliance. The Alliance lines coordinates public funding for projects like I405, Sound Transit, curved space, and traffic light coordination. It would provide the employer connection to those efforts in the Bothell geographic area from its life sciences community to SeaTac airport. | ||

|
EcoMotion: Electrifying Washington Park's Circulator for a Greener Future | |
| This project converts five existing Ford transit buses to electric power. This conversion not only reduces cost over buying new it ensures the gasoline engine is removed from the road and recycled instead of being sold for another use. It also retains the chassis and other equipment saving emissions over a new purchase. | ||

|
Electric Bus Deployments in Santiago de Chile | |
| An electric bus implementation program in Santiago, Chile, inspired by the buses in Bogotá, Colombia, began in 2014 through a partnership between the Chilean Ministry of Transport and two privately held companies, Enel X and BYD, an Italian electric company and a Chinese bus making manufacturer, respectively. | ||

|
Electric Island | |
| Electric Island is located across the street from DTNA headquarters, less than one mile from I-5, and represents the first location specifically designed for medium- and heavy-duty trucks aligned to the blueprint of the West Coast Clean Transit Corridor Initiative (WCCTCI). WCCTCI’s collaboration between nine electric utilities and two government agencies yielded a strategic plan in 2020 to electrify 1,300 miles of I-5 across the three West Coast states to provide publicly available charging for freight and delivery trucks. | ||

|
Electric Mobility Hub Demonstration | |
| An inviting & equitable community space that showcases electric mobility, integrates the street to the neighborhood, and serves as a model for future hubs. | ||

|
Electric Mobility Lab | |
| The EMS the Phase 0 Launch for the electric mobility initiative at Marine Corp Air Station Miramar. It included dynamic presentations from key government leaders on changing policies and plans, interactive panels with electric mobility thought leaders, as well as immersive demonstrations and discussions of technologies with industry-leading organizations. | ||

|
Electric Truck Charging Depot in Salem | |
| WattEV is planning to build an electric truck charging depot in Salem, Oregon, off Interstate 5, with the capacity to power approximately 40,000 trucks annually. | ||

|
Empowering Ruston City Services Using Wireless Sensor Networks | |
| The City of Ruston, Louisiana has a number of ongoing projects to improve the quality of life for its residents, including a Smart Grid system and a downtown fiber optic network. Louisiana Tech University plans to develop low-cost improvements to city services using the fiber-topic and small cell installations to enable smart transportation, smart weather, and smart flood risk monitoring and notification capabilities that can be viewed via a Smartphone App. We also plan to study the use of smart re-closers, wireless connectivity, and solar power potential. | ||

|
Empowering walkable and bikeable communities using smart Decision Support System integrated with Vehicle-to-Everything communication | |
| WIOMAX has developed a smart Decision Support System (DSS) integrated with Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) for better road safety and increased urban mobility. The main purpose of this project is to apply the smart transportation solution and incorporate pedestrians and cyclists as beneficiaries of the innovative technology, for empowering walkable and bikeable communities through enhancing road safety, sustainability and smartness of cities. | ||
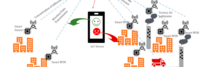
|
Environmental Sensing Across the Metro DC Region | |
| Create a network of environmental sensors placed on campuses throughout Washington DC that are participating in the DC MetroLab partnership. This effort will enable public access to environmental data like temperature, wind, gas and particulate concentration, and even traffic flows, simultaneously from all over the city. Involves city technology, planning, and networking agencies and MetroLab partners; George Washington, Georgetown, American, Howard and The District of Columbia Universities. | ||

|
EnvyPorto | |
| Through small and low cost sensing stations that can be installed in the urban infrastructure, it is possible to create a dynamic high level map of indicators on air quality, noise pollution levels, temperature, atmospheric pressure, humidity and luminosity. Using this high level map in articulation with the data collected using a small number of certified sensing stations (usually high-cost stations), cities will be able to define dynamic urban policies, namely on mobility and energy. | ||

|
Estimation of De Facto Population | |
Key Deliverables
| ||

|
Farm to Fork Crop Tracking | |
| Tracking a berry crop at the box, bin, or tote level from harvest in the field to end user. Monitor in near real time temperature, humidity, shock and other environmental conditions to ensure product quality after harvest, throughout transit and during storage. Potential to use blockchain to ensure authenticity of food safety certification which can travel with each sensor. | ||

|
Final 50 Feet: Urban Goods Delivery System | |
| The Final 50 Feet program looks at methods to improve delivery at the end of the supply chain, such as loading areas, traffic control and street design. We will pilot low-cost and high-value actions to optimize operations of goods. This will help us understand, maintain and enhance safer and efficient deliveries throughout a city and region. | ||

|
Full functioned Autonomous driving development park in Taiwan | |
Key Deliverables
| ||

|
Integrated Vehicle Service System | |
| The main purpose of the project is to expand the Smart Car project to next step - Smart Car system II that will enable citizens all kind of vehicle services, integrated into one system. The main target of this project is to guarantee advanced technologies and increase the type, accessibility and quality of the vehicle related public and private sector services from one point, online. | ||

|
Intelligent Transportation System applications in Kaohsiung City | |
| Create an intelligent traffic monitoring system connected to real-time Traffic Information System to reduce traffic congestion and raise the road safety in the city. Including telecom big data analysis for plan of traffic improvement strategy, congestion prediction and alert, intelligent parking guidance and Cooperative Vehicle-Infrastructure System for intersection safety. | ||

|
KPIs to Measure Urban Performance of 15 Min City | |
| KPIs to Measure Urban Performance of 15 Min City | ||

|
KPIs to Measure Urban Performance to measure the performance of 15 Min City | |
| 6 KPIs to Measure Urban Performance of 15 Min City. | ||

|
Kashiwanoha Smart City Project | |
| The Kashiwanoha smart city project (first described as Kashiwanoha International Campus Town Initiative) is a planned from scratch city project, involving a greenfield smart city vision, situated around Kashiwanoha Campus Station. Kashiwonoha smart city project is a privately-led project, with Mitsui Fudosan as the main developer. It was also the owner the previous owner of the golf course on which construction work of the project were first based. However, Kashiwa city was designated as one of the "FutureCities" by the national government in 2011, making Kashiwanoha new town project eligible for government subsidies. | ||
|
Minneapolis Mobility Hubs | |
| In 2019, the City of Minneapolis launched a mobility hub pilot program to increase access to convenient, low or no carbon transportation options, including transit, shared scooters and Nice Ride bicycles. | ||

|
Move PGH | |
| Move PGH unites diverse mobility services and created to provide Pittsburghers with more choices to get everywhere you need and want to go. Think of it as your one-stop-shop for all your transportation needs in the City of Pittsburgh. In coordination with the Department of Mobility and Infrastructure (DOMI) and powered by a group of the city's premiere mobility operators dubbed the Pittsburgh Mobility Collective, Move PGH will create a streamlined and accessible experience for car-free urban mobility. | ||
|
Multi-modal Trip Planner | |
| Develop a tool enables commuters to plan trips encompassing public transit, ride-sharing services, bike rentals, and pedestrian routes. By integrating multiple modes of transportation, this enhanced trip planner aims to make commuting more seamless and convenient, empowering individuals to choose sustainable alternatives to private vehicles. | ||

|
NoTraffic Pilot in Redlands CA | |
Key Deliverables
| ||

|
Oakland 100% electric school bus fleet | |
| The Oakland Unified School District, in collaboration with Zum and utility provider PG&E, has achieved a groundbreaking milestone by transitioning to a 100% electric school bus system with vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology. This initiative, the first of its kind in the US, involves a fleet of 74 electric buses equipped with bidirectional chargers managed through Zum's AI-enabled platform. By becoming emissions-free and serving as a Virtual Power Plant (VPP), this fleet not only addresses environmental concerns but also contributes 2.1 gigawatt hours (GWh) of energy back to the grid annually. This transformative project not only benefits the Oakland community but also sets a precedent for other districts, with plans to electrify school bus fleets in San Francisco and Los Angeles next. | ||

|
Open Data API Platform and Analysis of Taxi Dispatch | |
| Establish an Open data / API platform and integrate municipal and business data to be the foundation of the intelligent city for value-added applications. According to visually data display assist government to make decision effectively and let the citizen know the city governance. | ||
|
Portland Connected Intelligent Transportation | |
| This project focuses on developing a sensor-connected “smart” corridor in Portland where transit data, traffic signalization, and air quality sensing are made available in a data portal with data visualization and analytics to improve transportation options, public health, economic development and civic engagement. | ||

|
Portland Electric Avenue | |
| Electric Avenue officially opened at the World Trade Center Portland in 2016 and is located on the Northside of Southwest Salmon Street in downtown Portland. It offers street access charging stations to allow visitors to charge their personal electric vehicles while visiting the World Trade Center and neighboring offices. | ||

|
Public Transit Holland | |
| The Automicile project offers an integrated journey-planning platform for seamless urban and intercity travel across the Netherlands, combining convenience and accessibility for both residents and tourists. Through its user-friendly Journey Planner, travelers can select destinations such as Amsterdam, Rotterdam, and The Hague, or explore tourist spots like the Wadden Islands and Keukenhof, while choosing the fastest, cheapest, or most convenient travel options by metro, bus, tram, or train. Tickets, including national, international, and tourist tour options, can be booked online with an email confirmation and accessed via the Acompanion app. The platform also features a Tourist & Ticket Shop offering curated experiences, such as canal cruises and countryside tours, and a Pick-up Service for convenient collection of travel passes, ensuring a smooth and reliable experience for public transportation users. | ||

|
Reconnect Rondo | |
| The ReConnect Rondo project is a transformative initiative aimed at restoring and revitalizing the historic Rondo community in Saint Paul, Minnesota, which was devastated by the construction of Interstate 94 in the mid-20th century. At its core, the project envisions creating Minnesota’s first African American cultural enterprise district, anchored by a community land bridge that reconnects Rondo’s past vibrancy with a future of economic and social equity. This ambitious effort seeks to rectify historical wrongs, restore wealth and control to African American residents, and foster opportunities for businesses, housing, and leadership development within the community. Through collaborative partnerships with leaders, organizations, and policymakers, ReConnect Rondo is committed to ensuring equitable development, preventing gentrification, and creating a national model for restorative justice and sustainable community revitalization. | ||

|
Reduced customs clearance time with virtual extension of sea ports | |
| Develop and deploy electronic cargo tracking solutions in different settings (sea port, dry port and manufacturing FTZ) and across geographies (traversing from landlocked locations to ports, in East Africa and in Asia), for expedited customs clearance and enhanced trade facilitations. The solution is integrated across technology stacks, including end-devices, platforms and analytics, by ecosystem of accredited vendors. Involves security/field enforcement officials, customs officials, application developers, telco service providers, shippers and consignees. | ||

|
Smart Car Talk | |
Key Deliverables
| ||
![link=[[Media:{{{Release}}}]]](/images/thumb/0/08/Nagpur_Smart_Bus_Stop.jpg/200px-Nagpur_Smart_Bus_Stop.jpg)
![link=[[Media:{{{Release}}}]]](/images/thumb/9/9e/2030_bicycling_plan.jpg/200px-2030_bicycling_plan.jpg)















