Utility
| Utility | |
|---|---|
 Utility | |
| Team Members | City of Atlanta GA Gwinnett County GA City of San Leandro CA] Motorola Solutions CH2M Hill PilotCity Scalable Strategies |
| Blueprint | Utility |
This set of 52 projects is managed by the Utility team with the goal or addressing leading sustainability issues in cities for Energy, Water and Waste by bringing cities and counties together in the United States and around the world with academia and technology partners to demonstrate real world class examples and best practices. The SuperCluster is managed in three groups with each group managed with its own working group chair. Each Energy, Water and Waste working group is responsible for managing active projects with a common goal to develop a common blueprint. The blueprint will represent best practices and serve as a practical guide for the implementation IoT technologies
Objectives for the Utility SuperCluster include:
- Reduce water lost through leaks in water transmission and distribution utility infrastructure
- Increase water revenues with new and innovative metering technologies
- Increase water conservation adoption with weather analytics bases solutions
- Address city resilience needs with a focus on energy
- Develop and implement new strategies for zero waste
- Make it easy for cities to have access to public private partners funding models and government grant information
Chair(s)
-
[[File:|thumb|x{{{si{{{leader}}}e}}}px|link={{{leader}}}|{{{leader}}}
at
]]
Activities

|
An Open Architecture IoT Platform for a Sustainable Smart City | |
| BEMOSS®-Plus is an open-architecture platform that allows integration of IoT devices for energy savings, security, solar PV and storage in buildings. Its versatility will allow the management of energy usage (e.g., electricity and gas) for the entire city, including traffic and security monitoring. The project involves piloting BEMOSS®-Plus in Arlington County, the City of Alexandria and Virginia Tech university campus. | ||

|
Anatomy of a Smart City | |
| Showing the connecting fiber of a Smart City with Local Government, Public and Private Utilities and Services, Smart Building Technology, Communicating and sharing of Information to residents, business and the community as a whole with emphasis on security throughout the process. | ||

|
Beverly Public Schools Electric Busses | |
| Beverly Public Schools in Massachusetts has implemented a project utilizing their electric school buses as on-demand power plants. By using bidirectional chargers, the buses' large batteries can both charge and send energy back to the grid, providing backup power during high-demand periods. | ||

|
Bidirectional EV Charging Hub in British Columbia | |
| Pilot Project with BC Hydro, Lion Electric, BorgWarner, PowerTech Labs and Fermata Energy demonstrates Technical Feasibility as a Proof of Concept to Make Vehicle-to-Grid a Reality in British Columbia and Globally | ||
|
Calabar IoT-based Smart Waste Project | |
Objectives
| ||

|
Chula Vista Smart Waterfront | |
| The Chula Vista smart waterfront is a 535 acre joint development by City of Chula Vista and the Port of San Diego – currently the largest waterfront development project on the U.S. West Coast. The development is groundbreaking in its approach to energy efficiency in (1) targeting 50 percent reduction in annual energy use for the development and (2) each building performing at least 15 percent better than Title 24 requirements in the California Building Energy Efficiency Standards. Recognizing the need to monitor and control this new energy infrastructure, the Bayfront project also focuses on the communications network technologies and smart infrastructure solutions that will provide operational efficiency, sustainability, and economic development opportunities for the City. The Project team, led by Black & Veatch, is focused on evaluating the three major components of energy, telecom, and smart infrastructure – determining solutions that will meet the aggressive energy goals and provide a foundational, scalable approach to future communications and smart city applications. | ||

|
Digital Twin: Buildings As Batteries | |
| An innovative approach to digital twins that enables decentralization of power grids at unprecedented speed and scale. | ||

|
Direct Air Capture Plant in Oregon | |
| 280 Earth, Inc. has launched its inaugural Direct Air Capture (DAC) facility in The Dalles, Oregon, marking a significant milestone in the fight against climate change. | ||

|
Electric Island | |
| Electric Island is located across the street from DTNA headquarters, less than one mile from I-5, and represents the first location specifically designed for medium- and heavy-duty trucks aligned to the blueprint of the West Coast Clean Transit Corridor Initiative (WCCTCI). WCCTCI’s collaboration between nine electric utilities and two government agencies yielded a strategic plan in 2020 to electrify 1,300 miles of I-5 across the three West Coast states to provide publicly available charging for freight and delivery trucks. | ||

|
Electric Mobility Hub Demonstration | |
| An inviting & equitable community space that showcases electric mobility, integrates the street to the neighborhood, and serves as a model for future hubs. | ||

|
Electric Mobility Lab | |
| The EMS the Phase 0 Launch for the electric mobility initiative at Marine Corp Air Station Miramar. It included dynamic presentations from key government leaders on changing policies and plans, interactive panels with electric mobility thought leaders, as well as immersive demonstrations and discussions of technologies with industry-leading organizations. | ||

|
Electric Truck Charging Depot in Salem | |
| WattEV is planning to build an electric truck charging depot in Salem, Oregon, off Interstate 5, with the capacity to power approximately 40,000 trucks annually. | ||

|
Eton College Energy Station | |
| The installation of an innovative renewable "Energy Station" is helping GRAHAM to reduce its carbon footprint and power demands at Eton College. | ||

|
Flood Abatement | |
Predict Flooding & provide safety to human life, Current Project in Dunedin, NZ
| ||

|
Galway Smart City | |
| Galway has pioneered some smart city ideas. It has implemented an award winning 3 bin recycling scheme that achieved higher levels of recycling than any before seen in Ireland. Galway was the first city in Ireland to achieve the European Energy Award. It is involved in a number of projects to reduce energy usage and to lower the levels of carbon emissions. It adopted a smarter travel policy, including a new public transport strategy, various schemes to encourage citizen’s mobility (cycling and walking) and improved traffic management systems. The ‘slow the flow’ programme reduced the amount of drinking water being wasted in the City. In terms of education, Galway was possibly the first City in the world to achieve Green Flag status in all of its schools.
Galway Smart City - Light Pollution This project ensure the design of external lighting that minimizes the incidence of light pollution, glare and spillage into the surrounding environment and has due regard to the visual and residential amenities of surrounding areas. Galway Smart City - Air Quality and Noise This project aims for maintaining air quality to a satisfactory standard by regulating and monitoring atmospheric emissions in accordance with EU directives on air quality, by promoting and supporting initiatives to reduce air pollution, by increasing the use of public transport, developing urban woodland, encouraging tree planting and conserving green open space. | ||

|
Global High Impact Energy Efficiency | |
Objectives:
| ||

|
Gyeonggi Provincial virtual power plant in Gyeonggi Open Platform for Smart city | |
This is a project concept which is to create citizen-led, decentralized, local energy-based society that builds foundations on which the distributed resources (ESS, solar power) in the region that can proliferate profitable models which citizens invest, own, trade and operate.
| ||

|
IoT and AI based Smart Energy Management System for Smart City | |
| IoT & AI based Smart Energy Management Platform was deployed in public buildings in Suwon City to provide optimal management building facilities, environment, and energy using the urban 3D map and 3D spatial modeling. With the M&V (Measurement & Verification) engine using a standard algorithm, IPMVP (International Performance Measurement and Verification Protocol) as well as data intelligence technology with deep-learning, the platform can quickly measure energy performance and determine energy efficiency. | ||

|
IoT based waste management system-Smart Garbage Monitoring System | |
| Smart Garbage Monitoring System (SGMS) is a real time indicator of the level of trash at any given time. SGMS Optimize waste collection routes and ultimately reduce fuel consumption. It allows trash collectors to plan their daily/weekly pick up schedule. SGMS is to detect garbage level in Garbage Can. A unique identification number ( ID) is given to each can. As soon as the Garbage Can is full/ over flowing then a SMS is sent to the server from where all the garbage collection vehicles are allotted. | ||

|
IoT-based Smart Energy Management System for Smart Green City | |
The purpose of this research is to develop the convergence technologies of IoT-based smart energy management system that can minimize building energy use and utility bills. To accomplish the goal, The research objectives are proposed in the followings:
| ||

|
Kashiwanoha Smart City Project | |
| The Kashiwanoha smart city project (first described as Kashiwanoha International Campus Town Initiative) is a planned from scratch city project, involving a greenfield smart city vision, situated around Kashiwanoha Campus Station. Kashiwonoha smart city project is a privately-led project, with Mitsui Fudosan as the main developer. It was also the owner the previous owner of the golf course on which construction work of the project were first based. However, Kashiwa city was designated as one of the "FutureCities" by the national government in 2011, making Kashiwanoha new town project eligible for government subsidies. | ||

|
Leveraging Existing Automated Meter Reading for a Smart Alert Response Technology | |
| The City of Houston is 10,062 square miles (26,060 km²), with 6,950 miles (11,184 km) of sewer pipeline ranging in size from 6 to 144 inches (15 to 365cm) in diameter and including approximately 123,000 manholes. Houston uses the Automated Meter Reading (AMR)/Advanced Meter Infrastructure (AMI) network for identification and mitigation of Sanitary Sewer Overflows as part of the City's system-wide operation, maintenance and management plan. Houston calls this plan AIM (Automated Infrastructure Monitoring). | ||

|
Lighting Infrastructure as a Service Platform | |
| Lighting infrastructure is centrally located in city, close to people and activities. It provides excellent opportunity to collect and deliver information and services beyond lighting. Project targets to employ lighting infrastructure as the IoT backbone for different services in urban environments. | ||

|
Low Carbon Island and Smart Bay Project | |
| Penghu County is located on the central point of Taiwan Strait. The population of Penghu is 103, 000 in 2017 and there are about 1 million tourists visit Penghu per year. Since 2011 Penghu implemented the Low Carbon Island project and now will start the following second phase from 2018 to 2021. This project includes solar and wind power renewable energy development, offshore wind farm investment, smart grid system, electric vehicle, water and energy management system of small island and smart transportation service. | ||

|
Low-cost Air Quality Monitoring RAMPs in Pittsburgh PA | |
| The proposed project will deploy 30 Real Time, Multi-Pollutant Sensors (RAMPs) at traffic intersections currently managed by the Scalable Urban Traffic Control (SURTRAC) Intelligent Traffic control system, an adaptive traffic control system that optimizes traffic flows in the East Liberty corridor of Pittsburgh (see figure below). These RAMP sensors are portable, low-cost sensors for gaseous air pollutants and particulate matter (PM) that have been developed at Carnegie Mellon and will be mounted on utility poles, using the access already provided by SURTRAC for their equipment.
The existing SURTRAC architecture in East Liberty provides an important platform to study urban air quality through unprecedented approaches that could be replicated across city neighborhoods and which could eventually be scaled across the Pittsburgh metropolitan region. No other system like this currently exists. | ||

|
Non-Revenue Water Monitoring and Reduction Using Advanced LTE Communications Gwinnet County GA | |
| Install the first LTE communications base instrumentation in a pilot area and develop algorithms for understanding the elements of non-revenue water (lost water) as a means to reduce the cost of water delivery, improve management of scarce water resources, improve system operations, and save money for customers. The pilot will use advanced instrumentation with embedded LTE communications chips, such as smart water meters and pressure sensors to produce data to be used in the development of the software algorithms. | ||
|
Oil Gas well produced water localized treatment and recycle Coudersport Borough Eulalia Township PA USA | |
| Establish medium volume produced water treatment facilities near clusters of oil & gas well pads for localized treatment of the produced water. These facilities separate the produced water into metals for disposal, then salt for resale, and potable water for reuse or discharge to the local sanitation authority publicly owned treatment works (POTW). The facilities would be industrial waste water pre-treatment customers of the POTW. | ||

|
Online Power Quality Monitor for Electric Utilities and Municipalities | |
| Monitor Power Quality parameters such as voltage dips, sags, harmonics, THD, TDD and transients; monetize losses due to power quality; and minimize the troubleshooting time using our Power SCADA tool anywhere in Real Time. Get alarms and reports straight to your device in time. | ||

|
PGE Renewable Development Fund | |
| The PGE Renewable Development Fund awards grants for clean energy projects in the community. These are funded by PGE customers who choose Green Future renewable energy programs. | ||

|
Piloting lighting infrastructure as a service platform for smart lighting solutions | |
| Lighting infrastructure is centrally located in city, close to people and activities. It provides excellent opportunity to collect and deliver information and services beyond lighting. Project targets to employ lighting infrastructure as the IoT backbone for different services in urban environments. | ||

|
Pittsburgh building portfolio cyber-secure, real-time utility data integration and AI analysis | |
| This project is expanding on a successful 5 building pilot with the City of Pittsburgh to integrate most of the 167 city building’s real-time (15 minute interval) utility and usage data in the BuildFit application and BOSS Controls Smart Plugs. Using visualizations and artificial intelligence algorithms developed at the Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) School of Architecture (SOA), BuildFit will then provide recommendations for utility savings, sub-metering and indoor environmental quality (IEQ) optimization. The project will also allow for comprehensive support for the Pittsburgh Building Benchmarking Ordinance and Regional Energy Strategy (Power of 32) and 2030 District Challenge to improve energy resiliency and efficiency. Another important feature of the software and hardware components of this project will be defining and implementing the cyber security standards for smart building components and software in conjunction with NIST and other key government agencies. This will also include the first Smart Building/Smart City independent training, testing and certification lab at the Energy Innovation Center in Pittsburgh, PA | ||

|
Portland Electric Avenue | |
| Electric Avenue officially opened at the World Trade Center Portland in 2016 and is located on the Northside of Southwest Salmon Street in downtown Portland. It offers street access charging stations to allow visitors to charge their personal electric vehicles while visiting the World Trade Center and neighboring offices. | ||

|
PowerMatcher Blockchain Transactive Energy | |
| This project makes use of PowerMatcher a software developed in the Netherlands. | ||

|
ROSE - Real Time Operational Smart Grid for Europe | |
The ROSE project is
| ||

|
Resilience HUB - Vibrant Hawaii | |
| A goal of the Resilience Hub initiative is to build individual capacity and community networks to be resilient and ready for anything. To get there, Vibrant Hawai'i hosted a Resilience Leadership Academy (RLA) - a monthly development program with curated content by local experts. | ||

|
Smart City in the Sunshine State | |
The project includes the evaluation, selection and implementation of three main aspects of the County’s SCADA system:
| ||

|
Smart Replicable Solutions to Water-Energy Nexus Challenges | |
| The goal of this action cluster is to provide innovative solutions for managing drinking water, wastewater, stormwater and source water resources efficiently and effectively. | ||

|
Smart Waste Management & Logistics: Ecube Labs | |
Objectives
| ||
|
Smart Waste Management System | |
| Smart Waste is a system that enables direct cost reduction with easy to deploy smart sensor supporting up to 10 years of operational autonomy for remote waste container fill level measuring, geolocation, temperature, tilt, and collection routes optimization# Major flood event every year cause large amounts of residential and commercial damage | ||

|
Smart Waste Management and Logistics for Municipal Solid Waste Collection Operations | |
Objectives
| ||

|
Smart Water Technologies | |
| The goal of this action cluster is to provide innovative solutions for managing drinking water, wastewater, stormwater and source water resources efficiently and effectively.
The smart decisions that balance energy usage with desired water quality and quantity will be supported through the development of cloud-based analytics that is driven with the “Big Data” from distributed array of environmental sensors. These “Internet of Things (IOT)” environmental sensors will be used to both monitor and control the environment. The new data will be supplemented with the data from the existing infrastructure such as SCADA historian databases and meter data. Additional data needs will be examined carefully to reduce their impact on operations. For example, water meter data is usually collected on a daily basis to prolong the battery life whereas the same data may be needed at five-minute intervals to generate an accurate demand picture. Innovative approaches that provide additional data through low-cost sensing and citizen participation will be explored. | ||

|
Solar-Powered Truck Charging Depot | |
| WattEV's Bakersfield electric truck charging depot, spanning 119 acres, integrates a solar-powered microgrid with rapid megawatt charging, reducing truck dwell time to under 30 minutes. | ||

|
Solid Waste Management IoT Solution | |
| Garbage and refuse collection management is a critical function for any municipal government and private township. Inefficient or irregular collection leads to unsafe disposal by the public, which in turn creates conditions hostile to commerce and public health. Accelerite has developed an AWS solution on its Concert IoT platform that offers ready to use “Smart City” solid waste management IOT services.
The possibilities for creating public/ private sector revenue generating ecosystems are vast (e.g. selling recyclables and compostable waste to the highest bidder, revenue sharing with citizens to reward participation). Concert IoT’s Service Exposure and Monetization modules make it possible to expose services to partners for further innovation such that they can be consumed in a secure access and payments/settlements charging policy enforced manner. | ||

|
Southport development | |
| Southport is the only full-building solution available in the Greater Puget Sound area. As you enter Southport on Lake Washington you will quickly realize you are in a unique place. The entire campus has been designed with a focus on a lifestyle environment that supports the development of great teams. | ||
|
Taipei Smart City Programme | |
Taipei Smart City revolves around
| ||

|
Taoyuan City Water Resources Information System | |
| The core value of the System is to protect life and properties of people. The major purpose of developing the System is to apply technology of Smart Disaster Prevention and Internet of Things (IoT), and to build a resilient and sustainable city. | ||
|
The Great Lakes Smart and Sustainable Cities Cluster | |
| The Council of Great Lakes Region (CGLR) Regional Action Cluster will address the United Nations’ seventeen Sustainability Development Goals (SDGs) by consistently measuring sustainability at the neighborhood, city, state/provincial and regional levels. The cluster will also develop a framework to measure human well-being and ecosystem services by identifying bottom-up citizen co-creation actions taken across institutional boundaries. Open Action dashboards will display progress and link to knowledge achieving stated goals and objectives around the SDGs. | ||
|
Transactive Energy for Smart Cities | |
| This project makes use of PowerMatcher-IoT from project defined at http://www.powermatcher-iot.com which uses IEEE P1451.99 IoT Harmonization and an IoT Broker at http://www.ipdx.net software developed in Sweden. The project adds IoT XMPP to bridge any IoT protocol to provide cyber protection of privacy to meet Global Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) in the EU that can also be use else where including the US and facilitates data sharing for monetization of eDaler a new eDaler (Digital Currency) developed in Sweden and the United States. New CyberAI concerns will be evaluated to determine what conditions will require protection by allowing the owner of devices to determine what or who can control of situations in the city or if connected to an industrial or manufacturing facility that operation of a device does not create an unsafe condition for the plant or when used in a smart city that it does not potentially harm humans. | ||

|
Underground Infrastructure Sensing and Mapping | |
| Use sensing and information technology to determine the state of infrastructure and provide it in an appropriate, timely and secure format for the managers, planners and users. Information processing techniques convert the data in information-laden databases for use in analytics, graphical presentations, metering and planning. | ||

|
Urban Platform | |
| An easy-to-use platform that allows you to manage your city, whether you are responsible for traffic and mobility, safety, infrastructure or high-level decision making. | ||
Webinars

|
Energy Web Foundation | |
| Energy Web Foundation (EWF) has pioneered an enterprise-grade blockchain platform tailored to the sector’s regulatory, operational, and market needs. EWF is the world’s largest energy blockchain ecosystem—a growing community of over 100 energy market participants who we work with to bring energy blockchain solutions to market. The Energy Web has become the industry’s largest energy blockchain ecosystem and leading choice for decentralized technology powering the world’s energy future. | ||

|
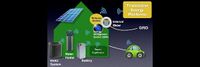
Grid Power Overview | |
| Overview of grid power | ||

|
The Evolution of the Built Environment | |
"At PGE, sustainability means business practices that support a vibrant economy, a healthy environment and strong communities today and into the future. It’s not a nice-to-have — it’s a must. As we make progress toward our environmental, social and governance goals, we’ll focus on how to become sustainable in everything we touch, including what we do for our customers."
| ||