Smart Buildings: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* [[https://opencommons.org/Interfacing_Smart_Buildings_with_City_Services_and_Infrastructure| Interfacing Smart Buildings with City Services and Infrastructure]] | * [[https://opencommons.org/Interfacing_Smart_Buildings_with_City_Services_and_Infrastructure| Interfacing Smart Buildings with City Services and Infrastructure]] | ||
* [[https://opencommons.org/Cybersecurity_for_Smart_Buildings| Cybersecurity for Smart Buildings]] | * [[https://opencommons.org/Cybersecurity_for_Smart_Buildings| Cybersecurity for Smart Buildings]] | ||
==Defining the Smart Building== | |||
A smart building is a building that uses technology and data to improve its energy efficiency, comfort, and functionality including the use of automatic control of the building's operations including heating, ventilation, air conditioning, lighting, security and other systems, maximizing user comfort while minimizing energy consumption. | |||
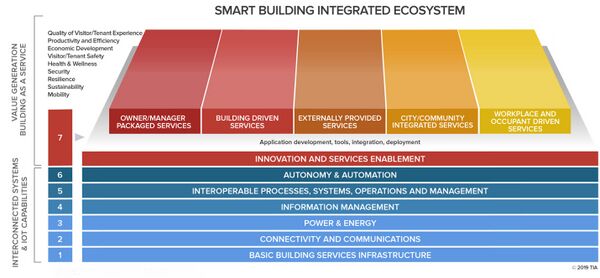
To maximize the opportunity smart building’s offer, it is important to set a foundation of understanding by defining what is a smart building. To that end, the smart building definition and model adopted by the SBSC as a guideline was developed by the [https://tiaonline.org/what-we-do/technology/programs/smart-buildings/ Telecommunications Industry Associations (TIA’s) Smart ][https://tiaonline.org/what-we-do/technology/programs/smart-buildings/ Buildings Program]. It defines a smart building as one which “interoperates and integrates systems, technologies and infrastructure to optimize building performance and occupant experience.” This creates the building which integrates and interoperates across fundamental building systems, communications infrastructure, power and energy infrastructure, through the use of data and autonomous, intelligent processing to provide any number of valued services to building owners, operators, occupants and visitors. Further, this smart, integrated system-of-systems built environment serves the needs of these stakeholders in real-time, providing the experience (contextualized data) when, where and how they want it. Now occupants and property owners can make informed decisions of what they want to do in and with that property. Through smart buildings systems and technologies, the property asset now becomes a platform that offers services – it enters the domain of ''Building as a Service'', and ''Space as a Service'' [[#Figure: Building as a Service/Space as a Service]]. | |||
<span align="center" id="Figure: Building as a Service/Space as a Service"></span> | |||
[[File:SmartBuildingIntegrationEcosystem.jpg|thumb|600px|center|<div style='text-align: center;'>'''Building as a Service/Space as a Service (Source TIA)'''</div>]] | |||
Revision as of 20:45, August 6, 2023
| Smart Buildings | |
|---|---|

| |
| Introduction | |
| Contact | Jiri Skopek |
| Topics | |
| NEWS
| |
- Authors
Smart Buildings is a fast-developing subject area.
Since the writing of the NIST Global City Teams Challenge [[1]] Smart Building Supercluster’s “[|Smart Buildings Blueprint]” in 2020 there have been significant advancements in this sector. This led to the need to update the blueprint with the latest information including references to the Smart Building KPIs, based on the NIST “[for Holistic Key Performance Indicators for Smart Cities (H-KPIs)]”
The online version follows the chapters of the original blueprint. These are:
- [Buildings O&M]
- [Organizational and Individual Productivity and Wellness of Smart Buildings]
- [Building-related Mobility]
- [Efficient and Connected Buildings (GEBs)]
- [Interfacing Smart Buildings with City Services and Infrastructure]
- [Cybersecurity for Smart Buildings]
Defining the Smart Building
A smart building is a building that uses technology and data to improve its energy efficiency, comfort, and functionality including the use of automatic control of the building's operations including heating, ventilation, air conditioning, lighting, security and other systems, maximizing user comfort while minimizing energy consumption.
To maximize the opportunity smart building’s offer, it is important to set a foundation of understanding by defining what is a smart building. To that end, the smart building definition and model adopted by the SBSC as a guideline was developed by the Telecommunications Industry Associations (TIA’s) Smart Buildings Program. It defines a smart building as one which “interoperates and integrates systems, technologies and infrastructure to optimize building performance and occupant experience.” This creates the building which integrates and interoperates across fundamental building systems, communications infrastructure, power and energy infrastructure, through the use of data and autonomous, intelligent processing to provide any number of valued services to building owners, operators, occupants and visitors. Further, this smart, integrated system-of-systems built environment serves the needs of these stakeholders in real-time, providing the experience (contextualized data) when, where and how they want it. Now occupants and property owners can make informed decisions of what they want to do in and with that property. Through smart buildings systems and technologies, the property asset now becomes a platform that offers services – it enters the domain of Building as a Service, and Space as a Service #Figure: Building as a Service/Space as a Service.
References
- ^ DigTwin2023


