Saitama City Smart Community Project: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|status=Implemented | |status=Implemented | ||
|website=http://www.misono-tm.org | |website=http://www.misono-tm.org | ||
|download= | |download=Saitama-SmartCity-Hiroaki-Nishi-0610.pdf | ||
|description=We developed a Smart Community Information Platform (SCIP) for achieving security and privacy management of smart city data and providing smart city data services considering time-, privacy-, and location- critical problems. We are implementing the information platform for providing smart town services for 32,000 residents in 230-hectare area of Misono Town, Saitama City as a testing site of SCIP. | |description=We developed a Smart Community Information Platform (SCIP) for achieving security and privacy management of smart city data and providing smart city data services considering time-, privacy-, and location- critical problems. We are implementing the information platform for providing smart town services for 32,000 residents in 230-hectare area of Misono Town, Saitama City as a testing site of SCIP. | ||
|challenges=We are tacking to establish a permanent system for providing attractive smart town services and to apply the system to other towns or cities as a standard model.<br \> | |challenges=We are tacking to establish a permanent system for providing attractive smart town services and to apply the system to other towns or cities as a standard model.<br \> | ||
Revision as of 06:19, April 26, 2022
| Saitama City Smart Community Project | |
|---|---|

| |
 Urban Design Center Misono, Saitama City | |
| Team Organizations | Keio University Kougakuin University Tokyo Denki University IIJ-II AEON UDCMi IBM SECOM Hitachi Panasonic TOSHIBA Tokyo Gas HONDA |
| Team Leaders | Hiroaki Nishi |
| Participating Municipalities | Saitama Japan |
| Status | Implemented |
| Document | 
|
Description
We developed a Smart Community Information Platform (SCIP) for achieving security and privacy management of smart city data and providing smart city data services considering time-, privacy-, and location- critical problems. We are implementing the information platform for providing smart town services for 32,000 residents in 230-hectare area of Misono Town, Saitama City as a testing site of SCIP.
Challenges
We are tacking to establish a permanent system for providing attractive smart town services and to apply the system to other towns or cities as a standard model.
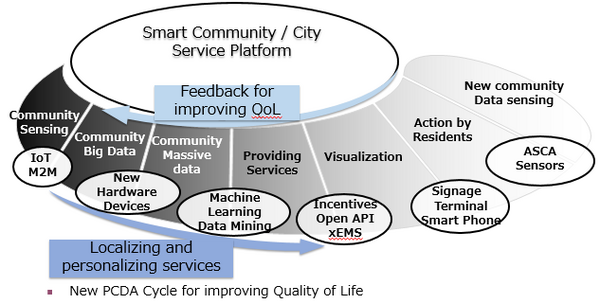
Solutions
We will provide smart town services for improving QoL of town residents and the town's brand power. We established a collaboration of local government, companies, and academics. The solutions to achieve the challenges is conducted under the collaborative organizations as shown in the figure of UDCMi structure. 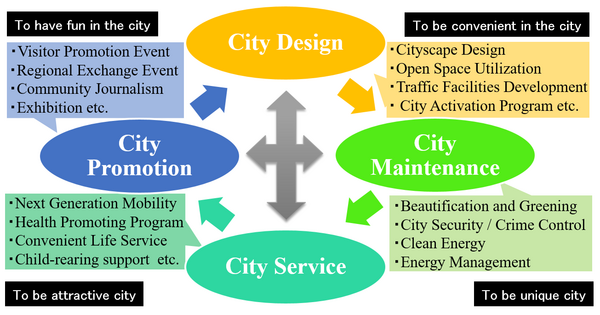
Major Requirements
- We established a consortium (Urban Design Center Misono: UDCMi) for developing an ICT infrastructure and smart town services under the collaboration of Saitama City, academics, and stakeholders.
- The following facilities are now available; 20 Smart Houses, 160 BLE beacon antennas and Wi-Fi infrastructures in the area, town monitoring systems, purchasing record using e-money card, activity records using activity sensors and a data management center in UDCMi.
- Smart town services will be provided by Integrating retailing information (AEON), security service (SECOM), data management platform (Keio Univ, Softbank), town signage (HITACHI), medical care (TANITA and local hospitals), and other information and services.
- We will provide permanent smart town services maintained by usage revenue of the services.
Performance Targets
| Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Measurement Methods |
|---|---|
|
- Total energy consumption will be reduced by 15% using distributed power generators, recommendation services, and point return services. |
- Total energy consumption is measured by the implemented automated metering infrastructure including smart meters. |
Standards, Replicability, Scalability, and Sustainability
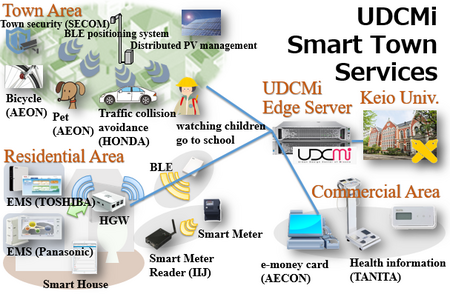
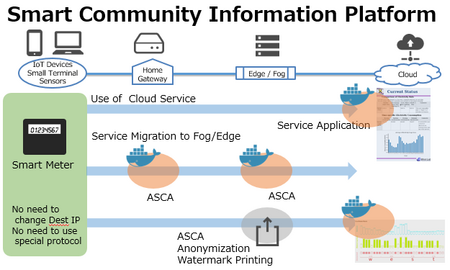


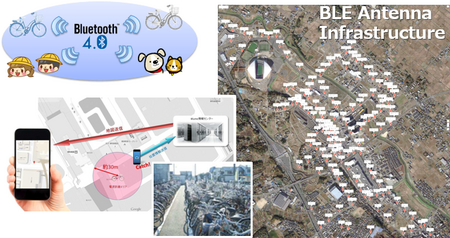
- The system uses privacy control method proposed as a deliverable of ITU-T Focus Group of Smart Sustainable City and the data infrastructure proposed in IEEE Standards Association Smart Grid Vision Project Documents.
- Some idea will be standardized in IEEE P21451 family. (Hiroaki Nishi is the Chair of IEEE P21451-9-1, and members of IEEE P2668, and 1451-99)
- All generated data of different infrastructures in the target town is integrated into smart community information platform (SCIP) using distributed networks, servers, and clouds, and service applications on SCIP are implemented as Docker containers for providing mobility in SCIP.
- SCIP API is an open library to design application software. It achieves secure and privacy-considered data interaction for data-oriented smart city services.
Cybersecurity and Privacy
- The designed SCIP enables to encapsulate resident’s data in a dedicated town. The data anonymization and watermarking technology for anonymized prevents and preparing unexpected data leaks.
- Authorized Stream Contents Analysis (ASCA) technology provides security services in the network devices.
Impacts
- SCIP is a sophisticated application execution infrastructure for smart city services including home gateways, routers, and cloud as execution locations, and it considers appropriate execution location and privacy level.
- UDCMi provides smart services, such as a location service using smart tag, and a mashup service of energy, health, medical, retailing, personal data.
- SCIP is a data anonymization infrastructure including privacy index management, anonymized data distribution management using watermark technology for anonymized data, and privacy policy management designed by integrating CRM and VRM.
- Machine learning technologies are used for providing services.
- It incubates new businesses of town services for the residents.
Demonstration/Deployment
- System demonstration is available at UDCMi.
- SCIP system demonstration was developed and achieved at the GCTC 2017 Exhibition. The demonstration is as follows:
-- Smart Meter measures the power consumption of houses.
-- As a general case, the measured data is directory transferred to a server in a cloud, and recommendation report of power usage is automatically generated by using machine learning techniques.
-- In this case, there is a possibility of the data leakage because the raw data of power consumption is directly transferred to the cloud.
-- In UDCMi system, locally installed network router monitor the packet stream to the cloud and anonymize the data at the router by using ASCA.
-- The service application on the cloud use the anonymized data. However, it can generate a recommendation report without critical errors. Moreover, the watermark of the data is implemented in the router.
-- The destination IP address of the stream is still set to the cloud.
System demonstration will be given at GCTC Expo in spring 2019.